Квентин Массейс: An Allegory of Folly
  |
| Автор |
Квентин Массейс
(1456/1466–1530) 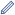  |
 |
| Альтернативные имена |
Quinten Massys (I), Quinten Matsijs, Quinten Matsys, Quinten Messijs, Quinten Messys, Quinten Metsijs (I), Quinten Metsys, Quintinus Metsys, Quintin Metsys |
| Описание |
Фламандский художник и рисовальщик |
| Дата рождения/смерти |
26 апреля 1466 / между 1465 и 1466 date QS:P,+1465-00-00T00:00:00Z/8,P1319,+1465-00-00T00:00:00Z/9,P1326,+1466-00-00T00:00:00Z/9  |
14 сентября 1530  |
| Место рождения/смерти |
Лёвен |
Антверпен |
| Место творчества |
|
| Авторитетный файл |
|
artist QS:P170,Q314275 |
|
| Название |
label QS:Len,"An Allegory of Folly" |
| Тип |
картина object_type QS:P31,Q3305213 |
| Дата |
начало XVI век date QS:P571,+1550-00-00T00:00:00Z/7 |
| Техника |
масло по деревуmedium QS:P186,Q296955;P186,Q106857709,P518,Q861259 |
| Размеры |
высота: 23,7 дюймов (60,3 см); ширина: 18,7 дюймов (47,6 см) dimensions QS:P2048,23.75U218593 dimensions QS:P2049,18.75U218593 |
| Коллекция |
New York, J. Held Collection |
| История владения (происхождения) |
1938: Norah Smith, Montreal, as 'Pieter Brueghel'. |
| Exhibition history |
- Worcester, Worcester Art Museum, The Worcester-Philadelphia Exhibition of Flemish Painting, 23 February - 12 March 1939.
- Philadelphia, J.G. Johnson Collection at the Philadelphia Museum of Art, 25 March - 26 April 1939, no. 45.
- Grand Rapids, Grand Rapids Art Gallery, Masterpieces of Dutch Art, 7-30 May 1940, no. 45.
- Indianapolis, John Herron Art Museum, Holbein and His Contemporaries, 22 October - 24 December 1950, no. 50.
- Poughkeepsie, Vassar College Art Gallery, Sixteenth Century Paintings from American Collections, 16 October - 15 November 1964, no. 8.
- Northampton, Smith College Museum of Art, Paintings and Sculpture from the Collection of Mr. and Mrs. Julius S. Held, 1-27 October 1968, no. 33.
|
| Надписи |
Текст вверху слева:
Mot./Mondeken/toe.
|
| Примечания |
In the early sixteenth century when Quentin Matsys painted his Allegory of Folly, likely around 1510, fools were still commonly found at court or carnivals, performing in morality plays. Sometimes a fool would be mentally handicapped, to be mocked for the amusement of the general public. Matsys has chosen to represent his fool with a wen, a lump on the forehead, which was believed to contain a "stone of folly" responsible for stupidity or mental handicap. In other instances, however, the fool would be a clever and astute observer of human nature, a comedian who used the fool's robes as a pretext for satire and ridicule. Matsys's fool was nearly an exact contemporary of Erasmus' Praise of Folly, in which the character of Folly is in fact a wise and astute commentator on folly in others. Fools were a popular subject in both the art and literature of this era and Erasmus' work was particularly important to the sixteenth-century Humanist circles in Antwerp.
The traditional costume of the fool includes a hooded cape with the head of a cock and the ears of an ass, as well as bells, here attached to a red belt. The fool holds a staff known as a marotte, or bauble, topped with a small carved figure of another fool - himself wearing the identifying cap. This staff would have been used as a puppet for satirical skits or plays, and the figure's obscene gesture of dropping his trousers, symbolic of the insults associated with fools, was once overpainted by a previous owner who found it overly shocking.
The gesture of silence, with the fool holding a finger to his lips, refers to the Greek god of silence, Harpocrates, who was generally depicted in this manner. Silence was considered a virtue associated with wise men such as philosophers, scholars, or monks. Here, however, Matsys turns the gesture into a parody by juxtaposing it with the inscription 'Mondeken toe', meaning 'keep your mouth shut', beneath the crowing cock's head. Matsys is drawing our attention to the Fool's indiscretion. A later hand has added the word 'Mot' above, likely a later sixteenth or seventeenth century reference to a prostitute - this may have been an attempt to turn the present allegory into the figure of a procuress.
Matsys' fool is made even more grotesque by his hideous deformities - an exaggerated, beaked nose and hunched back - and thin-lipped, toothless smirk. Grotesque figures were a favourite theme of the artist, making regular appearances in his paintings as tormenters of Christ or in allegories of Unequal Lovers. This reflects an awareness of the grotesque head studies of Leonardo da Vinci, whose drawings had made their way northward from Italy. Indeed, of all Matsys's other works, the fool in the present painting is perhaps closest in type to the tormenter directly behind and to the right of Christ in the Saint John Altarpiece - which is, itself, a direct quotation from Leonardo's own drawing of Five Grotesque Heads.
Quinten Matsys' early training is a matter of speculation, with scholars suggesting variously that he may have been apprenticed in Antwerp to Dieric Bouts; trained as a miniaturist in his mother's native town of Grobbendonk; or possibly worked for Hans Memling's studio in Bruges. We do know for certain that in 1494, Matsys was admitted to the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke as a master painter, and by the end of the century he was operating his own studio with several apprentices, among them his sons Cornelis and Jan. Matsys is known for both religious and secular works, and his style became increasingly Italianate in his later career; in turn he is recognized as an influence on such painters as Joos van Cleve, Joachim Patinir and Lucas Cranach the Elder. |
| Ссылки |
- F.F. Sherman, in Art in America, vol. 27, July 1939, p. 147, illustrated, under 'Recent additions to American Private Collections'.
- Art News Annual, vol. 37, no. 22, 1939, p. 56, illustrated.
- M.L. Wilson, The Tragedy of Hamlet Told by Horatio, Enschede, 1956, pp. 621-22, fig. 83.
- E. Tietze-Conrat, Dwarfs and Jesters in Art, London, 1957, pp. 19, 94, fig. 21.
- C.A. Wertheim Aumes, Hieronymous Bosch, Holland, 1961.
- W. Willeford, The Fool and His Scepter, Evanston, 1969, pp. 6, 29, pl. 2.
- L.A. Silver, Quentin Massys (1466-1530), Ph.D. diss., Harvard University, 1974, pp. 214-15, 355-56.
- A. de Bosque, Quentin Metsys, 1975, p. 196, no. 242, illustrated.
- S. Poley, Unter de Maske des Narren, Stuttgart, 1981, p. 47, fig. 39.
- L.A. Silver, The Paintings of Quinten Massys with Catalogue Raisonné, Montclair, 1984, pp.146-147, 192, 227-228, no.44, plate 135.
- C. Gaignebet et al., Art profane et religion populaire au moyen age, Paris, 1985, p. 189.
- Görel Cavalli-Bjorkman, 'The Laughing Jester', Nationalmuseum Bulletin, Stockholm, IX, 1985, no. 2, p. 106, fig. 7.
- S. Evans, Ben Jonson, PhD diss., University of Kansas, 1991.
- P. Lampert, Chronik der Bad Homburger Fastnacht, 1998, p. 100.
- M. Słowiński, Błazen. Dzieje postaci i motywu, Poznań, cover illustration.
|
| Источник/Фотограф |
http://www.christies.com/lotfinder/paintings/quentin-massys-an-allegory-of-folly-5176067-details.aspx |




